Managing Spasticity in Neurological Conditions
physiohealinghands
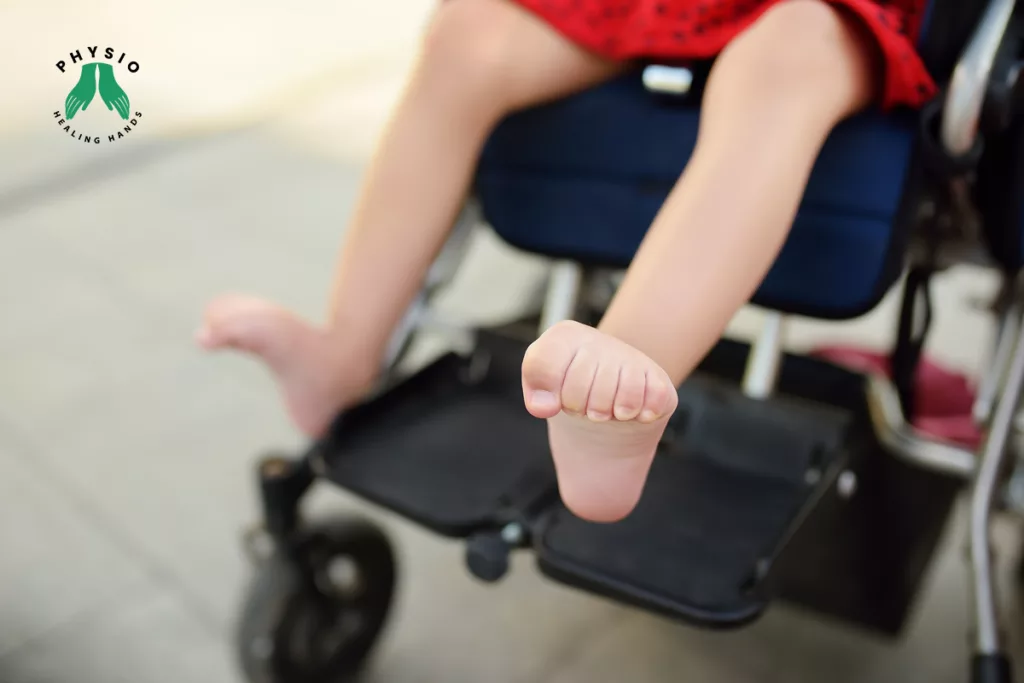

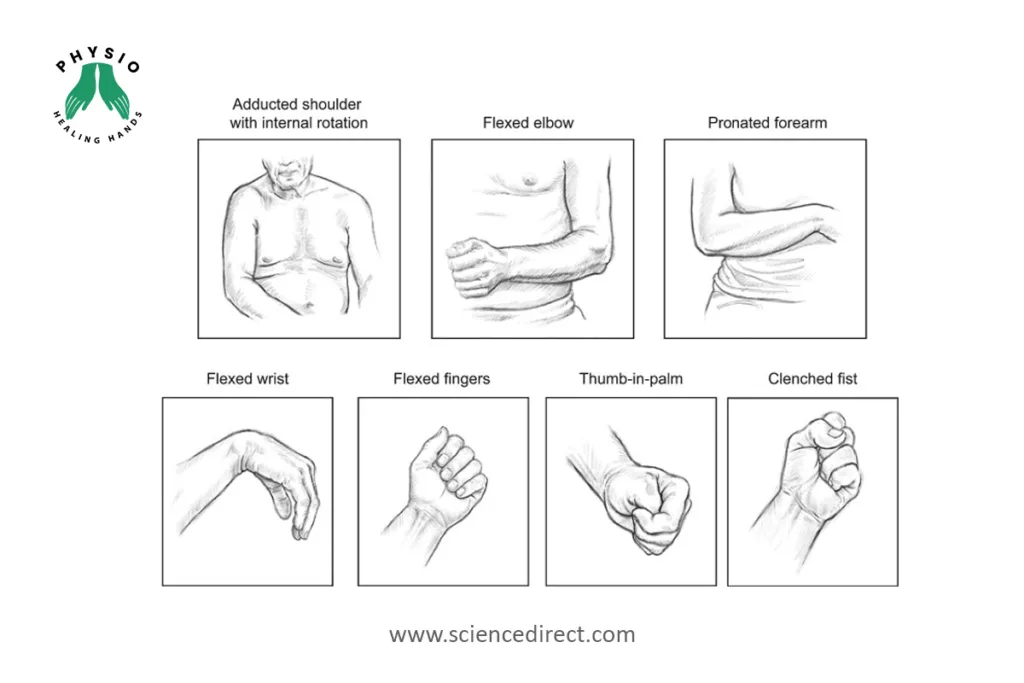
Spasticity is a common issue experienced by many individuals living with neurological conditions. It refers to the tightness or stiffness of muscles, often accompanied by involuntary muscle contractions. This can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, affecting their mobility, coordination, and overall function. However, there are effective strategies for managing spasticity. In this blog post, we will explore the techniques used by neurological physiotherapists to help individuals with neurological conditions effectively manage spasticity and improve their daily lives.
Understanding Spasticity: Before we delve into spasticity management, it’s essential to understand what causes it. Spasticity typically occurs due to damage or dysfunction in the central nervous system, such as the brain or spinal cord. Common neurological conditions associated with spasticity include stroke, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy, and spinal cord injury. When the communication between the brain and muscles is disrupted, the muscles can become hyperactive, leading to spasticity.
Spasticity Management Techniques
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing spasticity. Neurological physiotherapists are experts in assessing and treating spasticity-related issues. They develop personalized exercise programs targeting specific muscle groups to stretch and strengthen them. These exercises help maintain joint flexibility, prevent contractures (permanent muscle shortening), and improve overall mobility.
Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises
Range of motion exercises involve moving the joints through their full range to prevent stiffness and maintain flexibility. Physiotherapists use passive, active-assisted, or active ROM exercises depending on the individual’s abilities. These exercises improve joint mobility, reduce muscle tightness, and minimize the risk of contractures.
Stretching Exercises
Stretching exercises are designed to lengthen and relax the muscles affected by spasticity. Neurological physiotherapists employ various stretching techniques tailored to the individual’s needs. These exercises can be done manually by the therapist or with the help of stretching aids. Regular stretching helps reduce muscle stiffness, improves muscle balance, and enhances overall functional abilities.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises focus on improving muscle strength and stability. Neurological physiotherapists create individualized strength training programs that target specific muscle groups affected by spasticity. Strengthening weak muscles can help compensate for spasticity and improve overall movement control.
Functional Training
Functional training involves practicing everyday activities or tasks relevant to the individual’s daily life. It aims to enhance the person’s ability to perform these activities with greater ease and efficiency. Neurological physiotherapists help individuals with neurological conditions develop strategies and adaptive techniques to overcome the challenges posed by spasticity.
Assistive Devices and Technology
Neurological physiotherapists may recommend assistive devices or technology to aid individuals with spasticity. These may include braces, orthotics, walking aids, and adaptive equipment. Assistive devices and technology can provide additional support, improve mobility, and reduce the impact of spasticity on daily activities.
Modalities
In some cases, physiotherapists may utilize modalities such as electrical stimulation, heat therapy, or cold therapy to manage spasticity. These techniques can help relax muscles, reduce pain, and improve muscle function. However, the use of modalities is determined on an individual basis, and their effectiveness may vary.
Spasticity is a common challenge faced by individuals with neurological conditions. By working with a neurological physiotherapist, individuals can access specialized care and learn effective spasticity management techniques. Physical therapy, including range of motion exercises, stretching exercises, strengthening exercises, functional training, and the use of assistive devices, plays a vital role in managing spasticity. Remember, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to receive a personalized treatment plan based on your specific needs. With the right approach and support, individuals with neurological conditions can improve their mobility, reduce spasticity-related discomfort, and enhance their overall quality of life.
In addition to the techniques discussed above, there are several other approaches that can be beneficial in managing spasticity. Let’s explore them:
Splinting
Splinting involves the use of specialized braces or splints to support and immobilize specific joints or limbs affected by spasticity. Splints can help maintain proper alignment, prevent contractures, and reduce muscle tightness. They provide stability, promote proper positioning, and allow for functional use of the affected limb. Splinting can be particularly beneficial during rest or sleep to prevent the development of contractures and facilitate muscle relaxation.
K Laser (Low-Level Laser Therapy)
K Laser, also known as Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), is a non-invasive treatment that uses low-level laser light to stimulate cellular function. It has shown promise in managing spasticity by promoting tissue healing, reducing inflammation, and modulating pain perception. K Laser therapy can help improve muscle function, reduce muscle stiffness, and enhance overall motor control. It is typically used in conjunction with other spasticity management techniques to enhance outcomes.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese therapy that involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, acupuncture has been reported to have beneficial effects in managing spasticity. Acupuncture may help regulate muscle tone, improve blood circulation, and promote the release of endorphins, which are natural pain-relieving chemicals in the body. It can provide symptomatic relief, reduce muscle tightness, and improve overall functional abilities.
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy, also known as aquatic therapy, involves performing exercises and movements in a pool or aquatic environment. The buoyancy of water reduces the impact of gravity on the body, allowing for increased mobility and easier movement. Hydrotherapy can be particularly helpful for individuals with spasticity as the water provides resistance, aiding in muscle relaxation and improving joint range of motion. Additionally, the warmth of the water can help relax muscles and reduce pain, promoting a more comfortable and effective therapy session.
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) involves the use of electrical currents to stimulate targeted muscles, promoting muscle contraction and movement. FES can be beneficial in managing spasticity by improving muscle control, increasing strength, and facilitating functional movements. By delivering precise electrical stimulation to specific muscle groups, FES can help counteract spasticity-related muscle imbalances, enhance coordination, and improve overall motor function. FES is often used in combination with other therapeutic interventions to maximize its benefits.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these additional techniques may vary from person to person, and their usage should be determined on an individual basis. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a neurological physiotherapist, can help determine the most appropriate and effective spasticity management strategies for each individual.
Remember, managing spasticity requires a comprehensive and individualized approach. By combining different techniques and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with neurological conditions can optimize their spasticity management and improve their overall well-being.
Our Newsletter
Dig deeper into physiotherapy, health, and related topics that you care about by signing up for our newsletter.